Wireless Charging Principle of Electric Vehicle Design Case of Electric Vehicle Wireless Charging
Wireless Power Supply Resonant Capacitor for DER Electric Vehicle
Click Enter: New Energy Vehicle Wireless Charging Container Mall
Wireless Charging Special Resonant Capacitor for DER High Frequency and High Voltage Electric Vehicle
Resonant Circuit of Wireless Charging Pile for New Energy Electric Vehicle
Dielectrics: Special Materials
Structures: Special Materials and Metallized Membrane Inner Series Structures
Packaging: flame retardant Mylar tape, flame retardant (94V-0) epoxy packaging
Lead-out: Tin-plated copper nut or sheet lead-out
High ripple current capability
High stability, low loss
Self-healing
Working frequency: 20KHZ~85KHZ~150KHZ~200KHZ
With the progress of the times, electric vehicles have become a hot product of the industry, and new energy has become a hot topic for people to focus on. Compared with the wired charging of electric vehicles, wireless charging has the advantages of convenient use, safety and reliability, no danger of electric spark and shock, no dust accumulation and contact loss, no mechanical wear, no corresponding maintenance problems, and can adapt to the harsh weather and environment such as rain and snow.
1: Wireless Charging Principle of Electric Vehicle
At present, electromagnetic induction and magnetic resonance are mainly used in the wireless charging technology of electric vehicles.
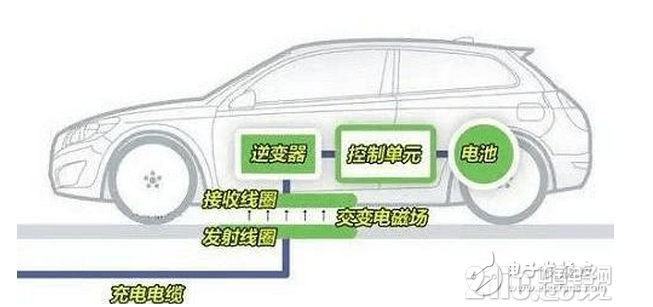
Compared with wired charging, the basic principle of wireless charging for electric vehicles is that there are more receiving coils and a simple charging interface.
Electromagnetic induction is a relatively mature technology at present. Many mobile phones charge wirelessly, even our common induction cooker is using this principle. A certain frequency AC of primary coil generates a certain current in secondary coil clock by electromagnetic induction, which transfers energy from the transmission end to the receiving end. When using, the distance between the two equipments must be very close, the power supply distance should be controlled between 0 mm and 10 cm, and the charging can only be done one to one with the alignment coil. Electromagnetic induction wireless charging has high energy conversion rate and large transmission power range, ranging from several to several kilowatts. The principle of magnetic resonance is similar to that of acoustic resonance. As long as two media have the same resonance frequency, they can transfer energy. The charging distance of this method between electromagnetic induction type and radio wave type has the advantage of large transmission power, which can reach several kilowatts. It can charge multiple devices at the same time without requiring coil correspondence between the two devices. The disadvantage is that the loss is very high, the farther the distance is, the larger the transmission power is, the greater the loss is, and the most troublesome is that the frequency band used must be protected.
2: Wireless Charging Technology for Electric Vehicles
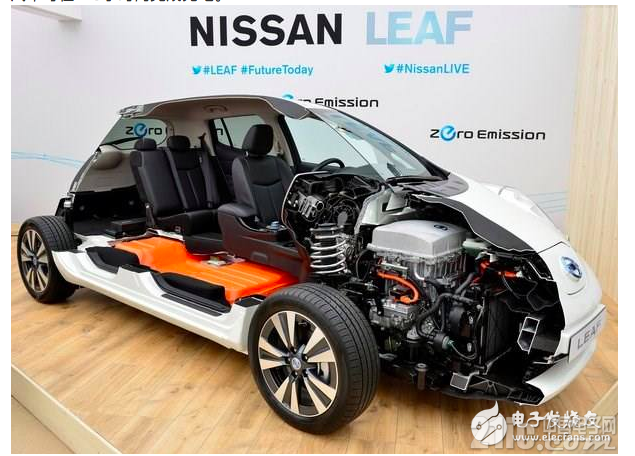
Nissan Magic Cube Electric Vehicle: It adopts the electromagnetic induction mode which can provide power between the power supply coil and the power supply coil. One coil device will be installed on the chassis of the car, and the other coil device will be installed on the ground. When the electric vehicle drives to the coil device, the coil will receive the current of the coil and charge the battery. At present, the rated output power of this device is 10 kW, and general electric vehicles can complete charging in 7-8 hours.
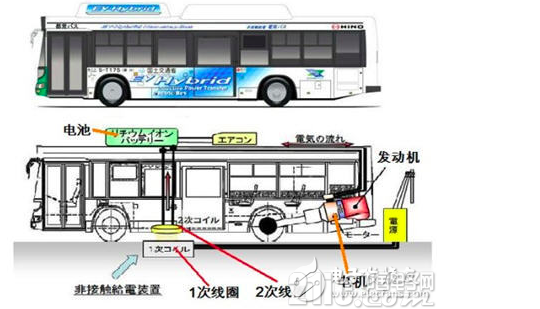
Japan Wireless Charging Hybrid Bus: Electromagnetic induction type, power supply coil is embedded in the concrete of the charging station. When the car is on the charging table, when the on-board coil is aligned with the power supply coil (coincidence), an indicator light will be on the dashboard of the car, and the driver will press the charging button to start charging.

At present, there are three kinds of wireless charging methods: electromagnetic induction charging, magnetic resonance charging and radio wave charging.
Electromagnetic induction charging: There is a certain frequency of alternating current in the primary coil, which generates current in the secondary coil through electromagnetic induction, thus transferring energy from the output end to the receiving end to complete wireless charging.
Magnetic resonance charging: The application of wireless charging technology originates from radio power transmission technology, which uses magnetic resonance to transmit charge in the air between charger and equipment, while coils and capacitors form resonance between charger and equipment to realize efficient transmission of electric energy.
Radio wave charging: It mainly consists of microwave transmitting device and microwave rece
iving device. As shown in the figure, the receiving circuit can capture the energy of the radio wave bouncing back from the wall and maintain a stable DC voltage while adjusting the load.
Generally speaking, the wireless power supply technology based on electromagnetic induction principle is the most realistic, and now it has practical application in electric vehicles. There are three problems in electromagnetic induction non-contact charging system: (1) the transmission distance is relatively short, if the transverse deviation of the two coils is large, the transmission efficiency will be significantly reduced. At present, the transmission distance is only about 10 cm, so many heat dissipation problems need to be considered, such as heating between coils. (2) For the coupled radiation problem, will there be a large leakage of magnetic field in the electromagnetic wave coupling? Electromagnetic induction transmits electricity between coils. Like our magnets, there is a certain leakage in the outer coil. How to avoid being affected is a big problem. (3) There may also be debris entering between the coils, and some animals (cats and dogs) entering the coils. Once the eddy current is generated, as in the electromagnetic oven, the safety problem is very obvious.



 iving device. As shown in the figure, the receiving circuit can capture the energy of the radio wave bouncing back from the wall and maintain a stable DC voltage while adjusting the load.
iving device. As shown in the figure, the receiving circuit can capture the energy of the radio wave bouncing back from the wall and maintain a stable DC voltage while adjusting the load.